7.25. Numerical Input Problem¶
Topic Contents
7.25.1. Overview¶
In numerical input problems, learners enter numbers or specific and relatively simple mathematical expressions to answer a question. The text that the learners enter is converted to a symbolic expression that appears below the response field.
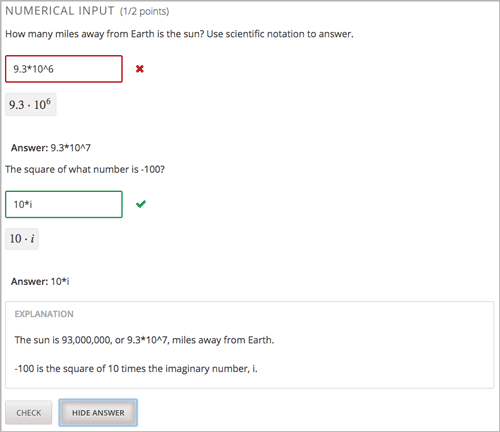
Responses for numerical input problems can include integers, fractions, and constants such as pi and g. Responses can also include text representing common functions, such as square root (sqrt) and log base 2 (log2), as well as trigonometric functions and their inverses, such as sine (sin) and arcsine (arcsin). For these functions, learners enter text that is converted into mathematical symbols. The following example shows a response entered by a learner and the numerical expression that results.
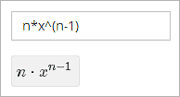
For more information about how learners enter expressions, see Math Response Formatting for Students.
You can specify a margin of error, or tolerance, for the answers to these problems so that learners’ responses do not have to be exact. You can specify a correct answer explicitly or use a Python script.
7.25.2. Analyzing Performance on Numerical Input Problems¶
For the numerical input problems in your course, you can use edX Insights to review aggregated learner performance data and examine submitted answers. For more information, see Using edX Insights.
7.25.3. Creating a Numerical Input Problem¶
You can create numerical problems in the Simple Editor or in the Advanced Editor.
- If the text of your problem does not include any italics, bold formatting, or special characters, you can create the problem in the Simple Editor.
- If the text of your problem contains special formatting or characters, or if your problem contains a Python script, you use the Advanced Editor.
For example, you must use the Advanced Editor to define the following problems.

In this example, the question uses a Python script to compute the square root.
For more information about including a Python script in your problem, see Write-Your-Own-Grader Problem.
7.25.3.1. Use the Simple Editor to Create a Numerical Input Problem¶
To the Simple Editor to create a numerical input problem, follow these steps.
- In the unit where you want to create the problem, under Add New Component select Problem.
- Select one of the two numerical input problem templates.
From the list of Common Problem Types, select Numerical Input.
From the list of Common Problems with Hints and Feedback, select Numerical Input with Hints and Feedback. For more information, see Use Feedback in a Numerical Input Problems.
Studio adds the problem to the unit.
- Select Edit. The Simple Editor opens.
- Replace the sample problem text with your own text.
- Determine the text that describes the question you want learners to answer,
and surround that text with two pairs of angle brackets (
>>question<<). This question text is the accessible label for the problem. question text is the accessible label for the problem. - To identify the problem’s answer, select the answer text and then select Numerical Input from the toolbar. An equals sign appears next to the answer.
- Optionally, specify a margin of error, or tolerance. You can specify a
percentage, number, or range.
- To specify a percentage on either side of the correct answer, after the answer add +-{number}%. For example, to include a 2% tolerance, add +-2%.
- To specify a number on either side of the correct answer, after the answer add +-{number}. For example, to include a tolerance of 5, add +-5.
- To specify a range, you provide the starting and ending values separated by a comma and then surround the range with brackets [] or parentheses (). A bracket includes the number next to it in the range, and a parenthesis excludes the number from the range. For example, if you specify [5, 8), correct answers can be 5, 6, and 7, but not 8. Likewise, if you specify (5, 8], correct answers can be 6, 7, and 8, but not 5.
- To provide an explanation, select the explanation text and then select
Explanation from the toolbar.
[explanation]appears before and after the explanation text. - Select Settings and provide an identifying Display Name for the problem.
- Define additional settings for the problem. For more information, see Problem Settings.
- Select Save.
For the first example problem illustrated above, the text in the problem component appears as follows.
>>What base is the decimal numeral system in?<<
= 10
[explanation]
The decimal numeral system is base ten.
[explanation]
7.25.3.2. Use the Advanced Editor to Create a Numerical Input Problem¶
For a more complex problem, such as the one that follows, you use the Advanced Editor.
- Follow the steps for creating the problem in the Simple Editor.
- Select Advanced Editor, and then edit the XML to add the tags and attributes you want. An example follows.
Problem Code:
<problem>
<p><b>Example Problem</b></p>
<legend>What base is the decimal numeral system in?</legend>
<numericalresponse answer="10">
<formulaequationinput label="What base is the decimal numeral system in?"/>
</numericalresponse>
</p>
<legend>What is the value of the standard gravity constant <i>g</i>, measured in m/s<sup>2</sup>? Give your answer to at least two decimal places.</legend>
<numericalresponse answer="9.80665">
<responseparam type="tolerance" default="0.01" />
<formulaequationinput label="Give your answer to at least two decimal places"/>
</numericalresponse>
<!-- The following lines use Python script spacing. Make sure it is not indented when you add it to the problem component. -->
<script type="loncapa/python">
computed_response = math.sqrt(math.fsum([math.pow(math.pi,2), math.pow(math.e,2)]))
</script>
<legend>What is the distance in the plane between the points (pi, 0) and (0, e)? You can type math.</legend>
<numericalresponse answer="$computed_response">
<responseparam type="tolerance" default="0.0001" />
<formulaequationinput label="What is the distance in the plane between the points (pi, 0) and (0, e)?"/>
</numericalresponse>
<solution>
<div class="detailed-solution">
<p>Explanation</p>
<p>The decimal numerical system is base ten.</p>
<p>The standard gravity constant is defined to be precisely 9.80665 m/s<sup>2</sup>.
This is 9.80 to two decimal places. Entering 9.8 also works.</p>
<p>By the distance formula, the distance between two points in the plane is
the square root of the sum of the squares of the differences of each coordinate.
Even though an exact numerical value is checked in this case, the
easiest way to enter this answer is to type
<code>sqrt(pi^2+e^2)</code> into the editor.
Other answers like <code>sqrt((pi-0)^2+(0-e)^2)</code> also work.
</p>
</div>
</solution>
</problem>
7.25.4. Use Feedback in a Numerical Input Problems¶
You can add feedback in a numerical input problem using the simple editor or the advanced editor. For an overview of feedback in problems, see Adding Feedback and Hints to a Problem.
In numerical input problems, you can provide feedback for correct answers.
Note
You cannot provide feedback for incorrect answers in numerical input problems.
Use feedback for the correct answer to reinforce the process for arriving at the numerical value.
7.25.4.1. Configure Feedback in the Simple Editor¶
In the Simple Editor, you configure answer feedback with the following syntax. When you create a new numerical input problem, select the template Numerical Input with Hints and Feedback. This template has example feedback syntax that you can replace.
= Numerical Answer {{Feedback for the correct answer.}}
For example, the following problem has feedback for each possible answer.
>>What is the arithmetic mean for the following set of numbers?
(1, 5, 6, 3, 5)<<
= 4 {{The mean for this set of numbers is 20 / 5 which equals 4.}}
7.25.4.2. Configure Feedback in the Advanced Editor¶
In the Advanced Editor, you configure answer feedback with the following syntax.
<numericalresponse answer="Correct Answer">
<formulaequationinput label="Question" />
<correcthint>
Feedback for the correct answer.
</correcthint>
</numericalresponse>
For example, the following problem has feedback for the correct answer.
<numericalresponse answer="4">
<formulaequationinput label="What is the arithmetic mean for the following
set of numbers? (1, 5, 6, 3, 5)" />
<correcthint>
The mean for this set of numbers is 20 / 5 which equals 4.
</correcthint>
</numericalresponse>
7.25.4.3. Customize Feedback Labels¶
By default, the feedback label for correct answers is Correct . If you do not define a feedback label, learners see this term when they submit a correct answer, as in the following example.
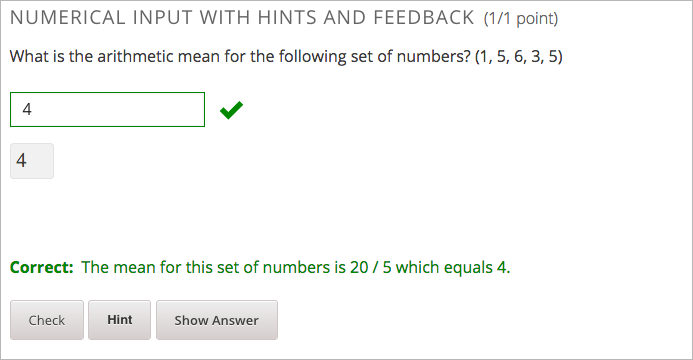
You can configure the problem to override the default labels. For example, you can configure a custom label for the answer.
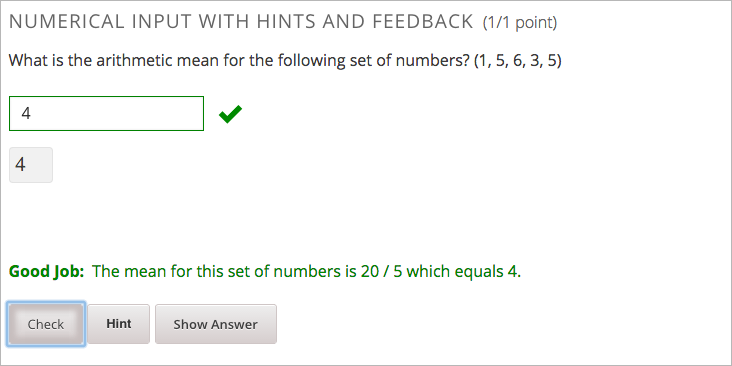
Note
The default label Correct is displayed in the learner’s requested language. If you provide a custom label, it is displayed to all users as you configure it and is not translated into different languages.
7.25.4.3.1. Customize Feedback Labels in the Simple Editor¶
In the Simple Editor, you configure a custom feedback label with the following syntax.
= 4 {{Label::Feedback}}
For example, the following feedback is configured to use a custom label.
= 4 {{Good Job::The mean for this set of numbers is 20 / 5 which equals 4.}}
7.25.4.3.2. Customize Feedback Labels in the Advanced Editor¶
In the Advanced Editor, you configure custom feedback labels with the following syntax.
<correcthint label="Custom Label">
Feedback
</correcthint>
For example, the following feedback is configured to use a custom label.
<correcthint label="Good Job">
The mean for this set of numbers is 20 / 5 which equals 4.
</correcthint>
7.25.5. Use Hints in a Numerical Input Problem¶
You can use hints in a numerical input problem, using the simple editor or the advanced editor. For an overview of hints in problems, see Adding Feedback and Hints to a Problem.
7.25.5.1. Configure Hints in the Simple Editor¶
In the simple editor, you configure hints with the following syntax.
||Hint 1||
||Hint 2||
||Hint n||
Note
You can configure any number of hints. The learner views one hint at a time and views the next one by selecting Hint again.
For example, the following problem has two hints.
||A fruit is the fertilized ovary from a flower.||
||A fruit contains seeds of the plant.||
7.25.5.2. Configure Hints in the Advanced Editor¶
In the advanced editor, you configure each hint in the <hint> element
within the <demandhint> element.
<demandhint>
<hint>Hint 1</hint>
<hint>Hint 2</hint>
<hint>Hint 3</hint>
</demandhint>
For example, the following XML shows two hints.
<demandhint>
<hint>A fruit is the fertilized ovary from a flower.</hint>
<hint>A fruit contains seeds of the plant.</hint>
</demandhint>
7.25.6. Numerical Input Problem XML¶
7.25.6.1. Templates¶
The following templates represent problems with and without a decimal or percentage tolerance.
7.25.6.1.1. Problem with No Tolerance¶
<problem>
<legend>TEXT OF PROBLEM</legend>
<numericalresponse answer="ANSWER (NUMBER)">
<formulaequationinput label="TEXT OF PROBLEM"/>
<correcthint>
Feedback for the correct answer.
</correcthint>
</numericalresponse>
<solution>
<div class="detailed-solution">
<p>TEXT OF SOLUTION</p>
</div>
</solution>
</problem>
7.25.6.1.2. Problem with a Decimal Tolerance¶
<problem>
<legend>TEXT OF PROBLEM</legend>
<numericalresponse answer="ANSWER (NUMBER)">
<responseparam type="tolerance" default="NUMBER (DECIMAL, e.g., .02)" />
<formulaequationinput label="TEXT OF PROBLEM"/>
<correcthint>
Feedback for the correct answer.
</correcthint>
</numericalresponse>
<solution>
<div class="detailed-solution">
<p>TEXT OF SOLUTION</p>
</div>
</solution>
</problem>
7.25.6.1.3. Problem with a Percentage Tolerance¶
<problem>
<legend>TEXT OF PROBLEM</legend>
<numericalresponse answer="ANSWER (NUMBER)">
<responseparam type="tolerance" default="NUMBER (PERCENTAGE, e.g., 3%)" />
<formulaequationinput label="TEXT OF PROBLEM"/>
<correcthint>
Feedback for the correct answer.
</correcthint>
</numericalresponse>
<solution>
<div class="detailed-solution">
<p>TEXT OF SOLUTION</p>
</div>
</solution>
</problem>
7.25.6.1.4. Answer Created Using a Script¶
<problem>
<!-- The following lines use Python script spacing. Make sure it is not indented when you add it to the problem component. -->
<script type="loncapa/python">
computed_response = math.sqrt(math.fsum([math.pow(math.pi,2), math.pow(math.e,2)]))
</script>
<legend>TEXT OF PROBLEM</legend>
<numericalresponse answer="$computed_response">
<responseparam type="tolerance" default="0.0001" />
<formulaequationinput label="TEXT OF PROBLEM"/>
<correcthint>
Feedback for the correct answer.
</correcthint>
</numericalresponse>
<solution>
<div class="detailed-solution">
<p>TEXT OF SOLUTION</p>
</div>
</solution>
</problem>
7.25.6.2. Tags¶
<numericalresponse>(required): Specifies that the problem is a numerical input problem.<formulaequationinput />(required): Provides a response field where the learner enters a response.<correcthint>(optional): Specifies feedback for the correct answer.<responseparam>(optional): Specifies a tolerance, or margin of error, for an answer.<script>(optional)
Note
Some older problems use the <textline math="1" /> tag instead
of the <formulaequationinput /> tag. However, the <textline math="1"
/> tag has been deprecated. All new problems should use the
<formulaequationinput /> tag.
Tag: <numericalresponse>
Specifies that the problem is a numerical input problem. The
<numericalresponse> tag is similar to the <formularesponse> tag, but
the <numericalresponse> tag does not allow unspecified variables.
Attributes
Attribute Description answer (required) The correct answer to the problem, given as a mathematical expression. Note
If you include a variable name preceded with a dollar sign ($) in the problem, you can include a script in the problem that computes the expression in terms of that variable.
The grader evaluates the answer that you provide and the learner’s response in the same way. The grader also automatically simplifies any numeric expressions that you or a learner provides. Answers can include simple expressions such as “0.3” and “42”, or more complex expressions such as “1/3” and “sin(pi/5)”.
Children
<responseparam><formulaequationinput><correcthint>
Tag: <formulaequationinput>
Creates a response field in the LMS where learners enter a response.
Attributes
Attribute Description label (required) Specifies the name of the response field. size (optional) Defines the width, in characters, of the response field in the LMS. Children
(none)
Tag: <responseparam>
Specifies a tolerance, or margin of error, for an answer.
Attributes
Attribute Description type (optional) “tolerance”: Defines a tolerance for a number. default (optional) A number or a percentage specifying a numerical or percent tolerance. Children
(none)
Tag: <correcthint>
Specifies a hint for the correct answer.
Tag: <script>
Specifies a script that the grader uses to evaluate a learner’s response. A
problem behaves as if all of the code in all of the script tags were in a
single script tag. Specifically, any variables that are used in multiple
<script> tags share a namespace and can be overridden.
As with all Python, indentation matters, even though the code is embedded in XML.
Attributes
Attribute Description type (required) Must be set to “loncapa/python”. Children
(none)
Tag: <demandhint>
Specifies hints available to the learner.
Children
<hint>
Tag: <hint>
Specifies a hint available to the learner.
Children
(none)