7.1. Working with HTML Components¶
This section describes how to work with HTML components in Studio.
7.1.1. HTML Component Overview¶
HTML, or HyperText Markup Language, is the standard markup language used to create web pages. Web browsers present HTML code in a more readable format.
When students see text and images in your course, they are seeing HTML code that is formatted and presented by their browsers. For more information about HTML, see Wikipedia.
7.1.1.1. HTML Components¶
HTML components are the basic building blocks of your course content. You use HTML components to add and format text, links, images, and more. You can work with your HTML components in a “visual” or WYSIWYG editor that hides the HTML code details, or in a “raw” editor that requires you to mark up your content.
Note
Review Developing Your Course and Use Best Practices for HTML Markup before you start working with HTML components.
To add an instant hangout to an HTML component, see Google Instant Hangout Tool.
7.1.2. Options for Editing HTML Components¶
You can use two different editing interfaces to work with an HTML component.
-
With the visual editor you create, edit, and format content in a word processing-like interface, without using HTML markup directly. With the visual editor, you can more easily format your content, and add links and images. The visual editor includes an HTML option for you to review the HTML markup and make small formatting changes to your content. However, this HTML option does not provide the detailed control you can get with the raw HTML editor, and does not support custom formatting or scripts.
If you add an HTML component and select Text, when you select Edit the visual editor opens by default.
-
If you prefer to mark up your content directly with HTML markup, you can use the raw HTML editor. If you need to include custom formatting or scripts in your content, you must use the raw HTML editor.
If you add an HTML component and select Raw HTML, when you select Edit the raw HTML editor opens by default.
You can switch back and forth between these two editing interfaces at any time. For more information, see Set the Editor for an HTML Component.
Note
If you copy text from another source and paste it into either the visual or raw HTML editor, be sure to proofread the result carefully. Some applications automatically change quotation marks and apostrophes from the “straight” version to the “smart” or “curly” version. Both editors require “straight” quotation marks and apostrophes.
7.1.2.1. Set the Editor for an HTML Component¶
- Add or locate the HTML component in your course.
- Select Edit, and then select Settings.
- Select Visual or Raw.
- Select Save, and then reopen the component to use the new editor.
Warning
If you work with content in the raw HTML editor, then switch to the visual editor, custom HTML can be lost. If you need to create custom HTML, edX recommends that you start by using the visual editor, and then switch to the raw HTML editor when you are ready to add the custom HTML.
7.1.3. The Visual Editor¶
The visual editor provides a “what you see is what you get” (WYSIWYG) interface that allows you to format text by selecting options at the top of the editor.
The following image shows callouts for the editing options and is followed by descriptions.
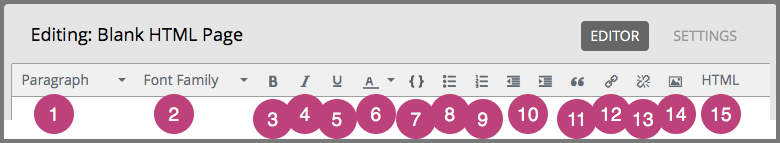
- Choose a formatting style for the selected text, such as paragraph,
preformatted(monospace), or a heading level. The heading levels available for an HTML component begin with Heading 3. Because HTML components are part of a complete page, and heading levels 1 and 2 are in use by other elements on the page, any text with a heading 1 or 2 style within an HTML component can interfere with the functionality of tools such as screen readers. - Choose a font family for selected text, such as Arial, Courier New, or Times New Roman.
- Format the selected text in bold, or remove bolding. The editor inserts
<strong>tags around the selected text. - Format the selected text in italics, or remove italicization. The editor
inserts
<em>tags around the selected text. - Underline the selected text, or remove underlining. The editor encloses the
selected text in the tag
<span style="text-decoration: underline;">. - Apply a color to the selected text. The editor encloses the selected text in
the tag
<span style="color: color-hex-code;">. - Format the selected text as a code block, or remove this formatting. The
editor inserts
<code>tags around the selected text, which is then displayed in a monospace font. - Create a bulleted list, or remove this formatting. The editor inserts
<ul>tags around the selected text, and encloses each paragraph in<li>tags. - Create a numbered list, or remove this formatting. The editor inserts
<ol>tags around the selected text, and encloses each paragraph in<li>tags. - Decrease and increased the indentation of the selected paragraph.
- Format the selected paragraph as a blockquote. The editor inserts
<blockquote>tags around the selected text, which is then displayed as a separate paragraph in a monospace font. - Create a hypertext link from the selected text. See Add a Link in an HTML Component.
- Remove a hypertext link from the selected text.
- Insert an image at the cursor. See Add an Image to an HTML Component.
- Review the HTML markup.
Note
The visual editor is not available for course handouts.
7.1.3.1. Review HTML Markup in the Visual Editor¶
To review the HTML markup added to content in the visual editor, select HTML from the visual editor’s toolbar. The HTML source code editor opens.
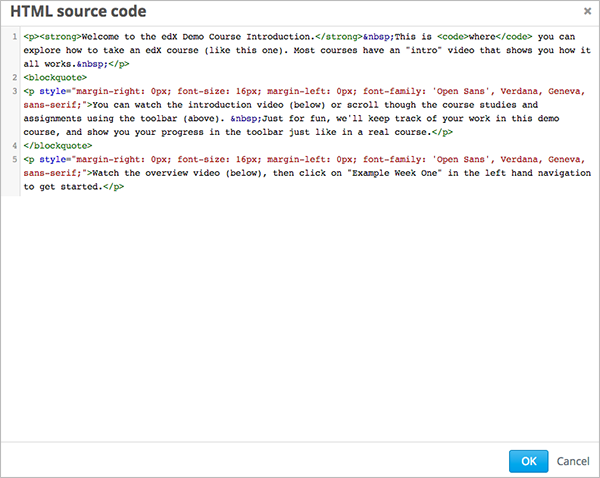
You can edit text and the HTML markup in this editor. However, you cannot add custom styles or scripts in this editor. Use the raw HTML editor instead.
Select OK to return to the visual editor. The visual editor attempts to correct any problems with the markup that you entered. For example, if you do not provide a close paragraph tag, the editor adds the tag for you.
You can then continue working in the visual editor.
Warning
Selecting OK in the source code editor does not save your changes to the HTML component. To save your changes and close the component, select Save in the visual editor. If you select Cancel, the changes you made in the HTML source code editor are discarded.
7.1.4. The Raw HTML Editor¶
The raw HTML editor is a text editor. It does not offer a toolbar with formatting options.
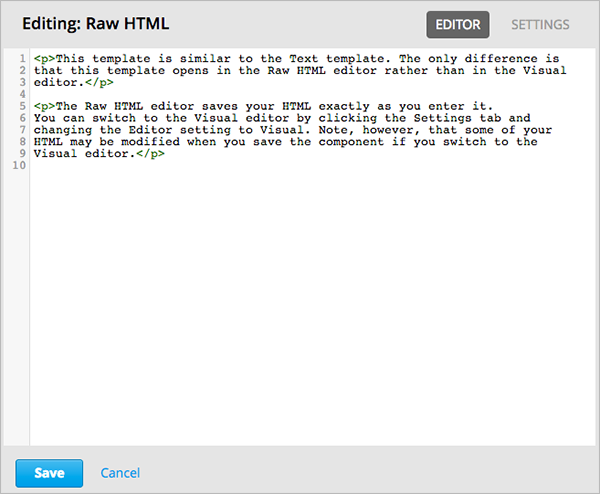
When you use this editor, you must supply valid HTML. The raw HTML editor does not validate your HTML code. If you use this editor, you should thoroughly test the HTML content in your course.
Important
Because HTML components are part of a complete page, any
text with a heading 1 or 2 style within an HTML component can interfere
with the functionality of tools such as screen readers. Be sure that the
headings you add to an HTML component are Heading 3 <h3> through Heading
6 <h6>, and not <h1> or <h2>.
7.1.5. HTML Component Templates¶
When you create an HTML component, you select from a list of templates.
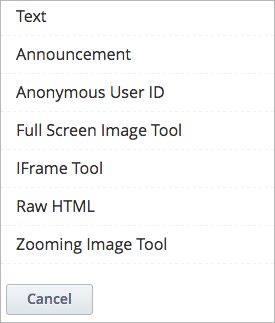
The raw HTML template uses the raw HTML editor by default. All of the other templates use the visual editor by default. You can switch between the editors in any HTML component. For more information, see Set the Editor for an HTML Component.
7.1.6. Create an HTML Component¶
Under Add New Component, select HTML.
Select the template.
The rest of these instructions assume that you selected Text, which creates an empty HTML component with the visual editor selected.
An empty HTML component appears at the bottom of the unit.
In the component, select Edit.
The HTML component opens in the visual editor.
Enter and format your content. You can review the HTML markup if needed.
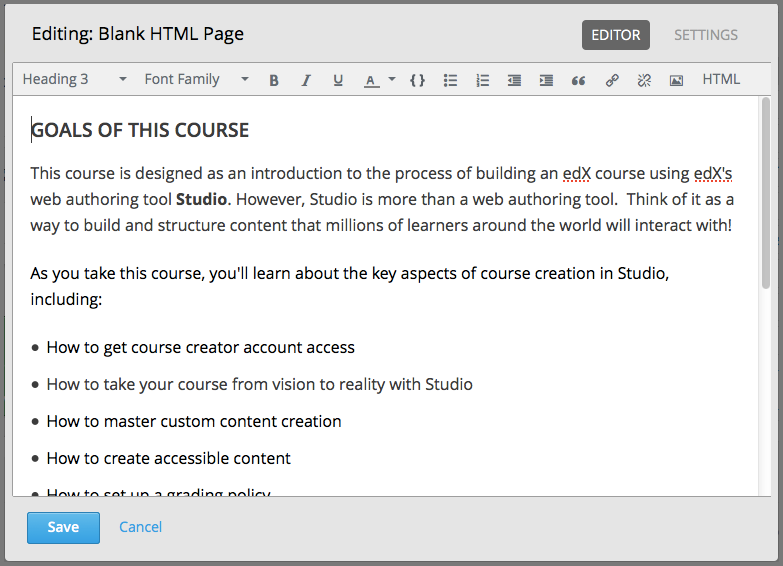
Enter a display name for the component. The display name identifies the component for learners, so it should describe the content effectively. To do so, select Settings, and then enter text in the Display Name field.
Each HTML template supplies a default display name. Changing the default to a unique, descriptive display name can help you and your learners identify course content quickly and accurately. If you delete the default display name and do not enter your own identifying name, the platform supplies “html” for you.
To return to the visual editor, select Editor.
Select Save.
When using the visual editor, you can also perform the following tasks.
7.1.7. Add a Link in an HTML Component¶
When using the visual editor, to add a link to a website, course unit, or file in an HTML component, you work with the Insert link dialog box.
For more information, see the following tasks.
7.1.7.1. Add a Link to a Website¶
Select the text that you want to use as the link text.
Select the link icon in the toolbar.
In the Insert link dialog box, enter the URL of the website that is the destination for your link.
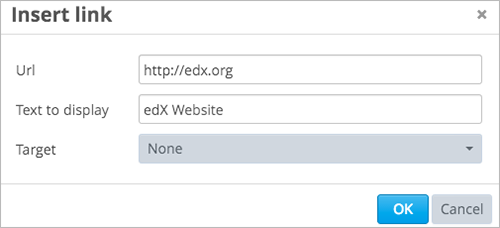
If you want the link to open in a new window, select the dropdown arrow next to the Target field, and then select New Window. If not, you can leave the default value.
Select OK.
Save the HTML component.
To test the link, select View Live Version or Preview. When the unit opens in the LMS, select the linked text and verify that the correct website opens.
7.1.7.2. Add a Link to a Course Unit¶
Note
To link to another component, the unit of that destination component must be published for the link to work.
Obtain the unit identifier of the unit you want to link to. To do this, open the unit page in Studio, and copy the unit ID from the Unit Identifier field under Unit Location in the right pane.
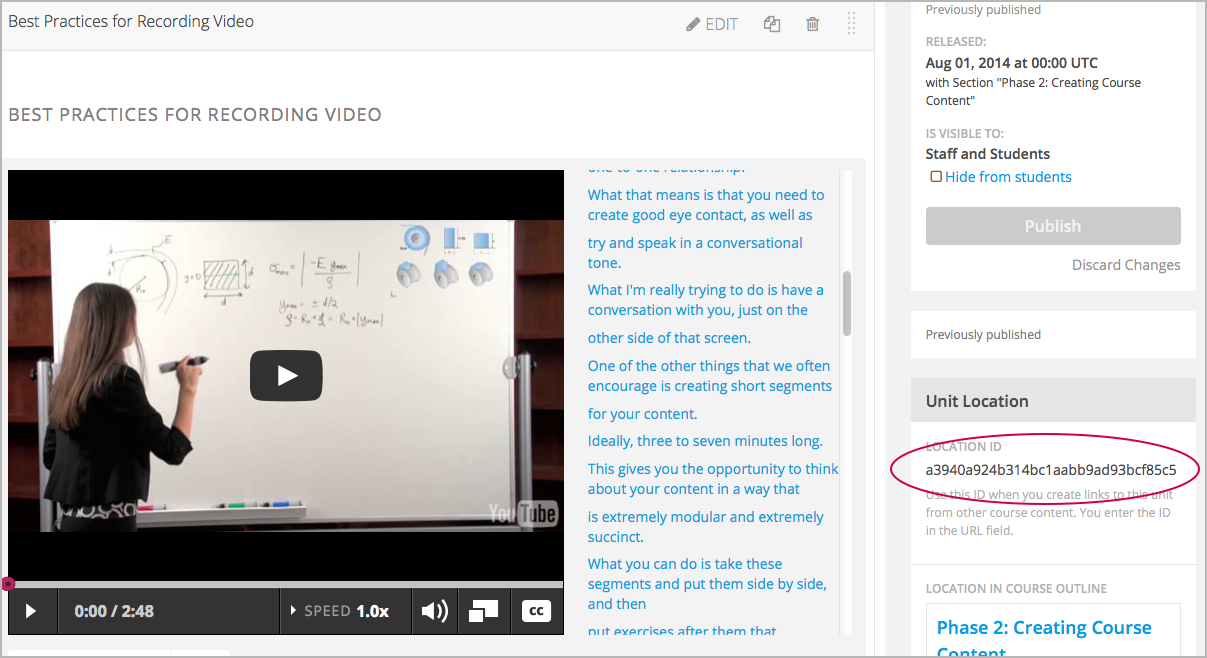
Open the HTML component where you want to add the link.
Select the text that you want to make into the link.
Select the link icon in the toolbar.
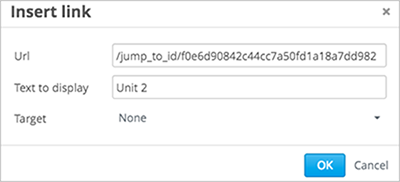
In the Insert link dialog box, enter the following in the URL field.
/jump_to_id/<unit identifier>Make sure to replace <unit identifier> (including the brackets) with the unit identifier that you copied in step 1, and make sure to include both forward slashes (/).
Caution
Ensure you use
/jump_to_id/<unit identifier>as the URL value. Do not use the URL of the unit that you see in the browser address bar. If you do not use/jump_to_id/<unit identifier>, the link will be broken if you export then import the course.
- If you want the link to open in a new window, select the dropdown arrow next to the Target field, and then select New Window. If not, you can leave the default value.
- Select Insert.
- Save the HTML component and test the link.
7.1.7.3. Add a Link to a File¶
You can add a link in an HTML component to any file that is uploaded for the course. For more information about uploading files, see Adding Files to a Course.
Tip
When adding links to files, open the HTML component and the Files & Uploads page in separate browser windows. You can then more quickly copy and paste file URLs.
- On the Files & Uploads page, copy the Studio URL of the file.
In the HTML component where you want to add the link, select the text that you want to make into the link.
Select the link icon in the toolbar.
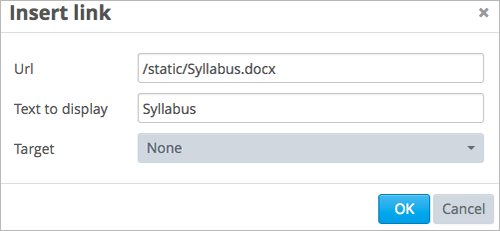
In the Insert link dialog box, enter the Studio URL for the file in the URL field.
/static/{FileName}.{type}Make sure to include both forward slashes (/).
If you want the link to open in a new window, select the dropdown arrow next to the Target field, and then select New Window. If not, you can leave the default value.
Select Insert.
Save the HTML component and test the link.
7.1.7.4. Add an Image to an HTML Component¶
When you use the visual editor, you can add any image that you have uploaded for the course to an HTML component. For more information about uploading images, see Adding Files to a Course.
Review Use Best Practices for Describing Images before you add images to HTML components.
Note
Ensure that you obtain copyright permissions for images you use in your course, and that you cite sources appropriately.
To add an image, you need the URL of the image that you uploaded to the course. You then create a link to the image in the HTML component.
Tip
When adding images, open the HTML component and the Files & Uploads page in separate browser windows. You can then more quickly copy and paste image URLs.
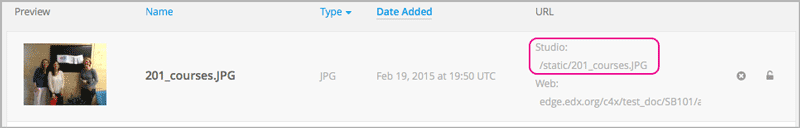
On the Files & Uploads page, copy the Studio URL of the image that you want. For an example illustration, see Add a Link to a File.
Note
You must use the Studio URL to add the image, not the Web URL.
In the HTML component where you want to add the link, select the image icon in the toolbar.
In the Insert image dialog box, enter the Studio URL for the file in the URL field.
/static/{FileName}.{type}Make sure to include both forward slashes (/).
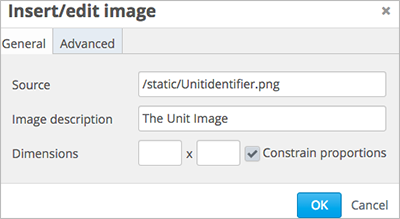
Enter alternative text in the Image description field. This text becomes the value of the
altattribute in HTML and is required for your course to be fully accessible. See Use Best Practices for Describing Images for more information.As needed, customize the image dimensions. Keep Constrain proportions selected to ensure the image keeps the same width and height proportions.
With Constrain proportions selected, you only change one dimension. When you tab out of the field, the other dimension changes to a value that maintains the same image proportions.
To change the spacing and border of the image, select the Advanced tab.
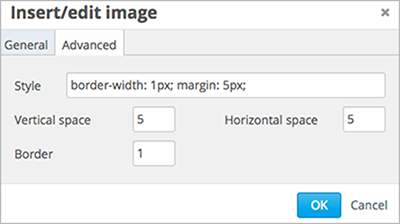
Enter the Vertical space, Horizontal space, and Border as needed. The values you enter are automatically added to the Style field.
Select OK to insert the image in the HTML component.
Save the HTML component and test the image.
7.1.7.5. Import LaTeX Code into an HTML Component¶
You can import LaTeX code into an HTML component. You might do this, for example, if you want to create “beautiful math” such as the following.
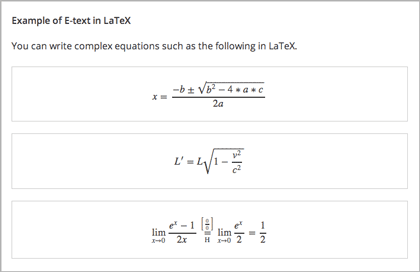
Warning
The LaTeX processor that Studio uses to convert LaTeX code to XML is a third- party tool. We recommend that you use this feature with caution. If you do use it, make sure to work with your partner manager.
7.1.7.5.1. Enable the LaTeX Processor¶
The LaTeX processor is not enabled by default. To enable it, you have to change the advanced settings in your course.
- In Studio, select Settings, and then select Advanced Settings.
- In the field for the Enable LaTeX Compiler policy key, change false to true.
- At the bottom of the page, select Save Changes.
7.1.7.5.2. Add an HTML Component that Contains LaTeX Code¶
When the LaTeX processor is enabled, you can create an HTML component that contains LaTeX code.
In the unit where you want to create the component, select html under Add New Component, and then select E-text Written in LaTeX. The new component is added to the unit.
Select Edit to open the new component. The component editor opens.
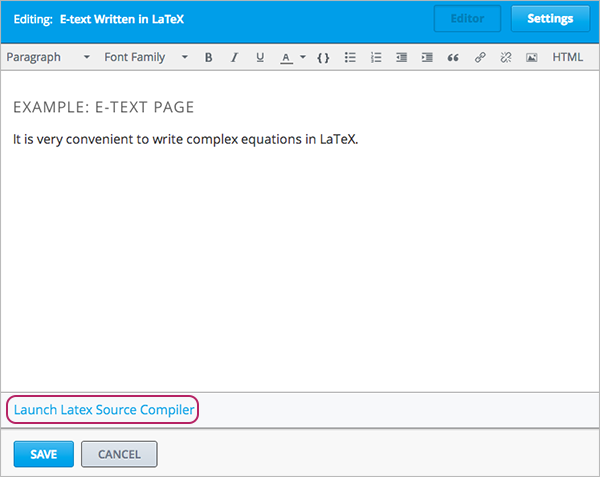
In the component editor, select Launch Latex Source Compiler. The LaTeX editor opens.
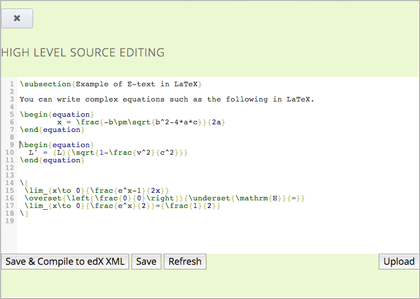
Write LaTeX code as needed. You can also upload a LaTeX file into the editor from your computer by selecting Upload in the bottom right corner.
When you have written or uploaded the LaTeX code you need, select Save & Compile to edX XML in the lower-left corner.
The component editor closes. You can see the way your LaTeX content looks.
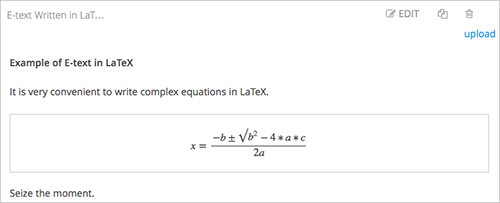
On the unit page, select Preview to verify that your content looks the way you want it to look in the LMS.
If you see errors, go back to the unit page. Select Edit to open the component again, and then select Launch Latex Source Compiler in the lower left corner of the component editor to edit the LaTeX code.