8.19. Math Expression Input Problems¶
In math expression input problems, students enter text that represents a mathematical expression into a field, and text is converted to a symbolic expression that appears below that field. Unlike numerical input problems, which only allow integers and a few select constants, math expression problems can include unknown variables and more complicated symbolic expressions.
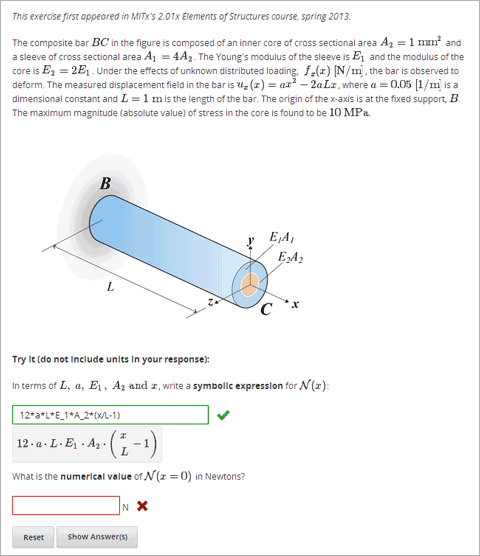
For more information about characters that students can enter, see Math Response Formatting for Students.
The grader uses a numerical sampling to determine whether the student’s response matches the instructor-provided math expression, to a specified numerical tolerance. The instructor must specify the allowed variables in the expression as well as the range of values for each variable.
Warning
Math expression input problems cannot currently include negative numbers raised to fractional powers, such as (-1)^(1/2). Math expression input problems can include complex numbers raised to fractional powers, or positive non-complex numbers raised to fractional powers.
When you create a math expression input problem in Studio, you’ll use MathJax to change your plain text into “beautiful math.” For more information about how to use MathJax in Studio, see A Brief Introduction to MathJax in Studio.
8.19.1. Create a Math Expression Input Problem¶
To create a math expression input problem:
- In the unit where you want to create the problem, click Problem under Add New Component, and then click the Advanced tab.
- Click Math Expression Input.
- In the component that appears, click Edit.
- In the component editor, replace the example code with your own code. To practice, you may want to use the sample problem code below.
- Click Save.
Sample Problem Code
<problem>
<p>Some problems may ask for a mathematical expression. Practice creating mathematical expressions by answering the questions below.</p>
<p>Write an expression for the product of R_1, R_2, and the inverse of R_3.</p>
<formularesponse type="ci" samples="R_1,R_2,R_3@1,2,3:3,4,5#10" answer="$VoVi">
<responseparam type="tolerance" default="0.00001"/>
<formulaequationinput size="40" label="Enter the equation"/>
</formularesponse>
<script type="loncapa/python">
VoVi = "(R_1*R_2)/R_3"
</script>
<p>Let <i>x</i> be a variable, and let <i>n</i> be an arbitrary constant. What is the derivative of <i>x<sup>n</sup></i>?</p>
<script type="loncapa/python">
derivative = "n*x^(n-1)"
</script>
<formularesponse type="ci" samples="x,n@1,2:3,4#10" answer="$derivative">
<responseparam type="tolerance" default="0.00001"/>
<formulaequationinput size="40" label="Enter the equation"/>
</formularesponse>
<solution>
<div class="detailed-solution">
<p>Explanation or Solution Header</p>
<p>Explanation or solution text</p>
</div>
</solution>
</problem>
8.19.2. Math Expression Input Problem XML¶
8.19.2.1. Templates¶
<problem>
<p>Write an expression for the product of R_1, R_2, and the inverse of R_3.</p>
<formularesponse type="ci" samples="R_1,R_2,R_3@1,2,3:3,4,5#10" answer="R_1*R_2/R_3">
<responseparam type="tolerance" default="0.00001"/>
<formulaequationinput size="40" label="Enter the equation" />
</formularesponse>
</problem>
<problem>
<p>Problem text</p>
<formularesponse type="ci" samples="VARIABLES@LOWER_BOUNDS:UPPER_BOUNDS#NUMBER_OF_SAMPLES" answer="$VoVi">
<responseparam type="tolerance" default="0.00001"/>
<formulaequationinput size="20" label="Enter the equation" />
</formularesponse>
<script type="loncapa/python">
PYTHON SCRIPT
</script>
<solution>
<div class="detailed-solution">
<p>Explanation or Solution Header</p>
<p>Explanation or solution text</p>
</div>
</solution>
</problem>
8.19.2.2. Tags¶
<formularesponse><formulaequationinput /><responseparam><script>
Tag: <formularesponse>
Specifies that the problem is a math expression input problem. The <formularesponse> tag is similar to <numericalresponse>, but <formularesponse> allows unknown variables.
Attributes
type: Can be “cs” (case sensitive, the default) or “ci” (case insensitive, so that capitalization doesn’t matter in variable names).
answer: The correct answer to the problem, given as a mathematical expression. If you precede a variable name in the problem with a dollar sign ($), you can include a script in the problem that computes the expression in terms of that variable.
samples: Specifies important information about the problem in four lists:
- variables: A set of variables that students can enter.
- lower_bounds: For every defined variable, a lower bound on the numerical tests to use for that variable.
- upper_bounds: For every defined variable, an upper bound on the numerical tests to use for that variable.
- num_samples: The number of times to test the expression.
Commas separate items inside each of the four individual lists, and the at sign (@), colon (:), and pound sign (#) characters separate the four lists. The format is the following:
"variables@lower_bounds:upper_bounds#num_samplesFor example, a
<formularesponse>tag that includes the samples attribute may look like either of the following.
<formularesponse samples="x,n@1,2:3,4#10">
<formularesponse samples="R_1,R_2,R_3@1,2,3:3,4,5#10">Children
<formulaequationinput />
Tag: <formulaequationinput />
Creates a response field where a student types an answer to the problem in plain text, as well as a second field below the response field where the student sees a typeset version of the plain text. The parser that renders the student’s plain text into typeset math is the same parser that evaluates the student’s response for grading.
Attributes
Attribute Description label (required) Specifies the name of the response field. size (optional) Specifies the width, in characters, of the response field where students enter answers. Children
(none)
Tag: <responseparam>
Used to define an upper bound on the variance of the numerical methods used to approximate a test for equality.
Attributes
Attribute Description default (required) A number or a percentage specifying how close the student and grader expressions must be. Failure to include a tolerance leaves expressions vulnerable to unavoidable rounding errors during sapling, causing some student input to be graded as incorrect, even if it is algebraically equivalent to the grader’s expression. type “tolerance”–defines a tolerance for a number Children
(none)